ETFs (exchange-traded funds): A Comprehensive Guide to Smart Investing
What Are ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds)?
ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) are investment funds that trade on stock exchanges, similar to individual stocks. They offer a diversified portfolio of assets, including stocks, bonds, commodities, or a mix of asset classes. ETFs have become a popular investment choice due to their flexibility, low cost, and ease of trading.
Why Invest in ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds)?
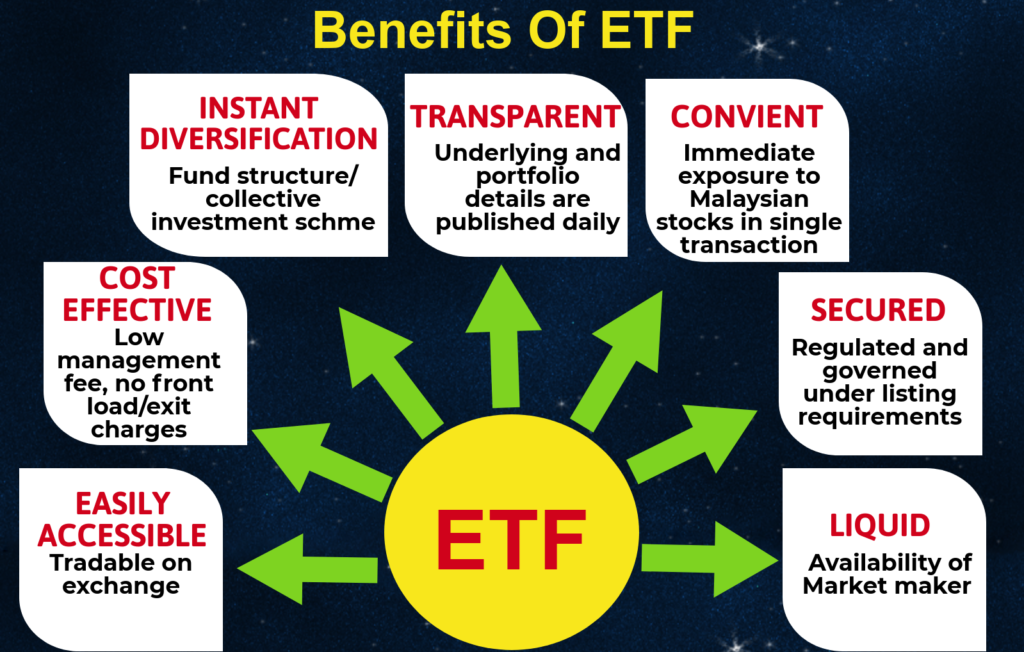
Benefits of ETFs
- Diversification – ETFs provide exposure to a variety of assets, reducing risk.
- Liquidity – They trade on exchanges, allowing investors to buy and sell throughout the trading day.
- Cost-Effectiveness – ETFs often have lower expense ratios than mutual funds.
- Transparency – Holdings are usually disclosed daily, offering insight into asset allocation.
- Tax Efficiency – ETFs are structured to minimize capital gains taxes for investors.

Types of ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds)
1. Stock ETFs
Stock ETFs track indexes like the S&P 500, Nasdaq, or specific sectors, allowing investors to gain broad exposure to the stock market.
Popular Stock ETFs
- SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY)
- Invesco QQQ Trust (QQQ)
- Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI)
2. Bond ETFs
Bond ETFs invest in fixed-income securities, providing income and stability.
Common Bond ETFs
- iShares Core U.S. Aggregate Bond ETF (AGG)
- Vanguard Total Bond Market ETF (BND)
3. Commodity ETFs
These ETFs allow investors to gain exposure to commodities like gold, silver, oil, and agricultural products.
Examples of Commodity ETFs
- SPDR Gold Shares (GLD)
- United States Oil Fund (USO)
4. Sector and Industry ETFs
Sector ETFs focus on specific industries, such as technology, healthcare, or energy.
Top Sector ETFs
- Technology Select Sector SPDR Fund (XLK)
- Health Care Select Sector SPDR Fund (XLV)
5. International ETFs
International ETFs provide exposure to foreign markets, including developed and emerging economies.
Examples of International ETFs
- Vanguard FTSE Developed Markets ETF (VEA)
- iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ETF (EEM)
6. Thematic ETFs
These ETFs focus on specific investment themes, such as artificial intelligence, clean energy, or blockchain technology.
Examples of Thematic ETFs
- Global X Robotics & Artificial Intelligence ETF (BOTZ)
- iShares Global Clean Energy ETF (ICLN)
7. Dividend ETFs
Dividend ETFs focus on companies that pay high dividends, providing a steady income stream.
Notable Dividend ETFs
- Vanguard Dividend Appreciation ETF (VIG)
- iShares Select Dividend ETF (DVY)
Read also Source: Quora
How to Choose the Right ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds)?
Factors to Consider
- Investment Goals – Define your objectives, whether it’s growth, income, or diversification.
- Expense Ratio – Look for ETFs with low management fees.
- Liquidity – Ensure the ETF has high trading volume and low bid-ask spreads.
- Underlying Assets – Analyze the assets held by the ETF to ensure they align with your strategy.
- Performance History – Compare past performance against benchmarks.
- Tax Efficiency – Understand how distributions and capital gains impact taxation.
How to Invest in ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds)?
Steps to Get Started
- Open a Brokerage Account – Choose a platform that offers commission-free ETF trading.
- Research ETFs – Use financial tools to analyze ETF performance and holdings.
- Place a Trade – Buy ETFs like stocks, choosing market or limit orders.
- Monitor Your Portfolio – Regularly review performance and rebalance as needed.
Risks Associated with ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds)
Market Risk
ETFs are subject to fluctuations in the market, which can lead to potential losses.
Liquidity Risk
Some ETFs, especially niche or low-volume ones, may have higher spreads and lower liquidity.
Tracking Error
ETFs may not always perfectly replicate the performance of their underlying index due to fees and management strategies.
Sector-Specific Risks
Thematic and sector ETFs may experience volatility based on industry trends and regulations.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What Are ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds)?
ETFs are investment funds that trade on stock exchanges and offer diversified exposure to various asset classes.
Are ETFs Better Than Mutual Funds?
ETFs often have lower fees, more liquidity, and greater tax efficiency compared to mutual funds.
Can ETFs Lose Money?
Yes, like any investment, ETFs can decline in value due to market fluctuations and economic conditions.
How Are ETFs Taxed?
ETFs generally have lower capital gains taxes than mutual funds, but dividends and sales are still subject to taxation.
What Is the Minimum Investment for ETFs?
There is no minimum investment for ETFs, but investors must buy at least one share.
Conclusion
ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) offer a versatile and cost-effective way to diversify portfolios and achieve financial goals. Whether investing in stocks, bonds, commodities, or thematic trends, ETFs provide accessibility and efficiency for both beginners and experienced investors. Understanding the different types, risks, and strategies involved ensures smarter investment decisions and long-term success.




